Introduction.
Boiler systems are the heart of many residential and commercial heating setups. These systems play a crucial role in providing warmth and hot water for various applications. In this detailed guide, we will explore what boiler systems are, how they work, the various types available, their efficiency, advantages, disadvantages, troubleshooting tips, and crucial information on maintenance and replacement costs.
What is a boiler system?
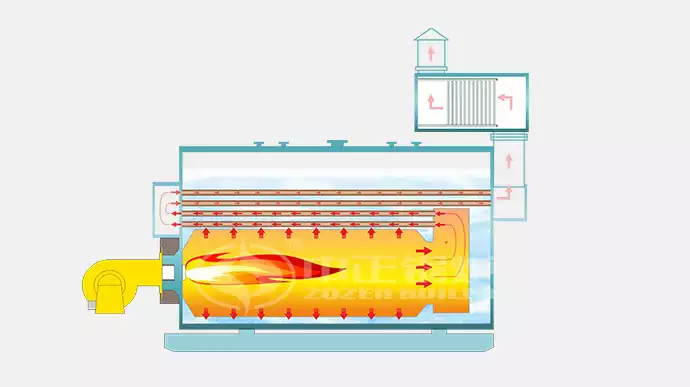
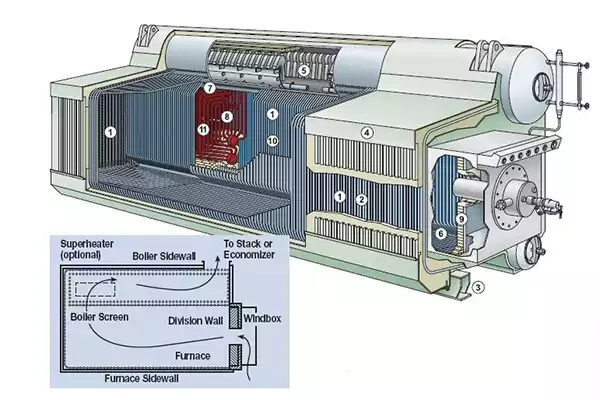
A boiler system is a heating device that generates hot water or steam to distribute heat throughout a building, serving both residential and industrial needs. They are commonly found in homes, factories, hospitals, and power plants. The core purpose of a boiler system is to transfer thermal energy from a fuel source to water or another medium, which is then circulated through pipes and radiators or used for other heating applications.
How does a boiler system work?
Boiler systems work on the principle of heat transfer. Fuel, such as natural gas, oil, electricity, or biomass, is burned within the boiler to produce heat. This heat is then transferred to water or a heat transfer fluid, resulting in the production of hot water or steam. The hot water or steam is then distributed through a network of pipes to radiators, baseboards, or underfloor heating systems to provide warmth.
Types of boiler systems.
Boiler systems come in various types, each with its unique features and applications. Here are some common types:
Combi boiler system
A combi (combination) boiler combines both heating and hot water production in a single unit. They are space-efficient and well-suited for small to medium-sized homes. They heat water on demand, providing an endless supply of hot water.
Condensing boiler system
Condensing boilers are highly efficient as they recover heat from exhaust gases, improving energy utilization. They are eco-friendly and often recommended for energy-conscious consumers.
Biomass boiler System
Biomass boilers use organic materials like wood pellets or agricultural waste as fuel. They are considered environmentally friendly and are popular in areas with abundant biomass resources.
Electric Boiler system
Electric boilers use electricity as their energy source, making them easy to install and maintain. They are ideal for homes without access to natural gas or oil.
Efficiency of boiler systems.
The efficiency of a boiler system is a crucial factor in determining its operating costs. Modern boiler systems are designed to be highly efficient, with some reaching up to 98% efficiency. Higher efficiency means less wasted energy and lower cost.
Boiler systems are more efficient than gas or electric heating, which can lose up to 30% of their energy. They also offer greater efficiency than oil heating and wood burning.
Advantages of a boiler system.
Boiler systems have several advantages over other types of heating systems. They are:
Efficient – Boiler systems use less energy than other types of heating, such as electric heaters or radiators. This means you’ll save money on your monthly bills and have more money to spend on other things.
Easy to Install – A boiler system is easy for plumbers to install because all the equipment is contained in one unit that can be placed anywhere in your home or business building.
Cheaper To Operate – Because boilers use less energy than other types of heaters, they cost less money each month when compared to what people pay when using an electric heater instead (or vice versa).
Easy to use and maintain – Boiler systems have fewer parts than other types of heating systems, which means there’s less that can go wrong with them during their lifespan. You also don’t need any special training or certifications in order to operate a boiler yourself.
Safe and reliable – A boiler system is designed to run continuously, so you don’t have to worry about your heating system failing at an inopportune time. If there’s a problem with the heat in your home, you’ll know right away because it will be obvious that something is wrong.
Disadvantages of a boiler system
Installation costs
Complexity adds to costs: The installation cost of a boiler system can vary widely depending on the type and complexity of the system. High-efficiency boilers, radiant heating systems, or large-scale industrial boilers often require intricate installation processes, which can substantially increase upfront expenses.
Piping and ventilation: Properly setting up a boiler system necessitates not only the boiler unit but also an extensive network of piping, ventilation, and sometimes additional equipment like expansion tanks or pumps. These components add to the overall installation expenses too.
Space requirements
Physical footprint: Boilers come in various sizes, but even compact residential units can occupy a considerable amount of space. This can be a significant limitation in homes or buildings with limited available space.
Piping and ventilation: The network of pipes, ducts, and ventilation systems necessary for the operation of a boiler can be extensive. Allocating space for these components, especially in retrofitting existing structures, can be challenging and may require structural modifications.
Maintenance
Safety concerns: Boiler systems operate under high pressure and temperature conditions. Neglecting maintenance can lead to safety hazards, such as leaks or even catastrophic failures. Regular inspections and servicing are vital to ensure the system remains safe for occupants.
Efficiency degradation: Without proper maintenance, boiler efficiency can decline over time. This can result in higher energy bills and reduced heating performance. Components like burners, heat exchangers, and controls must be cleaned, calibrated, and replaced when necessary to maintain peak efficiency.
Carbon emissions
Many traditional boiler systems rely on fossil fuels like natural gas or oil, which release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants when burned. This can contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change.
Boiler system troubleshooting
Loss of heat or hot water supply
Possible causes:
- Low fuel supply or pressure.
- A malfunctioning thermostat.
- Airlocks in the pipes.
- Faulty circulator pump.
Repair steps:
- Check fuel supply and pressure; refill if necessary.
- Verify that the thermostat is set to the desired temperature.
- Bleed air from the radiators or pipes to remove airlocks.
- Inspect the circulator pump for any signs of damage or malfunction and replace it if necessary.
Boiler leaks
Possible causes:
- Corrosion or rust.
- Damaged seals or gaskets.
- Pressure relief valve issues.
Repair steps:
- Identify the source of the leak.
- For minor leaks, try tightening or replacing damaged seals or gaskets.
- If the pressure relief valve is leaking, it may need replacement.
- For severe corrosion, it may be necessary to replace the affected boiler components.
Strange noises (e.g., banging or whistling)
Possible causes:
- Air trapped in the system.
- Sediment buildup in the boiler.
- Water hammer (sudden pressure changes).
Repair steps:
- Bleed air from radiators or pipes to eliminate air pockets.
- Flush the boiler system to remove sediment.
- Install water hammer arrestors to reduce pressure fluctuations.
Boiler overheating or rapid cycling
Possible causes:
- Incorrect thermostat settings.
- Faulty temperature sensor.
- Water pressure issues.
Repair steps:
- Check and adjust the thermostat settings to the desired temperature.
- Test the temperature sensor and replace it if malfunctions.
- Ensure proper water pressure within the system; adjust as needed.
Pilot light or ignition problems (gas boiler system)
Possible causes:
- Gas supply issues.
- Faulty ignition system.
- Blocked pilot or burner.
Repair steps:
- Check the gas supply, ensure the gas valve is open, and relight the pilot light following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect and clean the ignition system, including the spark igniter or thermocouple.
- Remove any obstructions in the pilot or burner assembly.
Pressure loss
Possible causes:
- Water leaks.
- Faulty pressure relief valve.
- Expansion tank issues.
Repair steps:
- Address any water leaks as mentioned earlier.
- Test and replace the pressure relief valve if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Inspect the expansion tank and replace it if it’s waterlogged or damaged.
Electrical failures (electric boiler system)
Possible causes:
- Tripped circuit breakers.
- Faulty wiring or heating elements.
Repair steps:
- Check and reset any tripped circuit breakers or replace any blown fuses.
- Inspect the wiring and heating elements for damage and replace them if necessary.
Malfunctioning controls and safety features
Possible causes:
- Faulty thermostats or pressure switches.
- Malfunctioning safety cut-off switches.
Repair steps:
- Test and replace any faulty controls, sensors, or switches as needed.
- Ensure that safety features like high-pressure or temperature cut-offs are functioning correctly.
- In order to troubleshoot a boiler system, you need to know how it works so that you can recognize what’s going wrong when something goes wrong!
When do I replace my old boiler system?
If you are experiencing problems with your boiler system, it may be time to replace it. Here are a few signs that there’s something wrong with your heating system:
- It’s not working properly. If your boiler isn’t heating up the water in your home, or if there are other issues like frequent leaks and clogs, then this could indicate that it needs repairs or replacement.
- The age of the unit is too old. Over time, boilers can become less efficient and more costly to maintain as they get older–and eventually, they will need replacing altogether!
- Repair costs are high compared to buying a new one outright. This is especially true if you have an older model that uses outdated technology (like oil-fired or gas-fired heat pumps) which don’t meet current efficiency standards set by government agencies like energy star.
How much does it cost to replace a boiler system?
In general, the average cost for a complete replacement could range anywhere from $2,000-$10,000. The cost of replacing a boiler system can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of boiler, its size, the complexity of the installation, geographic location, and any additional features or upgrades you choose.
| Type of boiler system | Estimated cost range (Including installation) |
|---|---|
| Gas boiler | $3,000 – $6,000 |
| Oil boiler | $4,000 – $8,000 |
| Electric boiler | $2,500 – $5,000 |
| Biomass boiler | $5,000 – $10,000 |
| Condensing boiler | $7,000 – $12,000 |
| Combi boiler | $3,500 – $7,500 |
How much is a new boiler system?
The price of a new boiler system depends on the type and size. For instance, a standard boiler system can cost between $2,500 and $7,500, while more complex systems may exceed $10,000.
| Type of boiler system | Estimated cost range (Boiler unit) |
|---|---|
| Gas boiler | $2,500 – $5,000 |
| Oil boiler | $3,000 – $6,500 |
| Electric boiler | $1,500 – $3,500 |
| Biomass boiler | $3,500 – $7,500 |
| Condensing boiler | $5,500 – $12,000 |
| Combi boiler | $4,000 – $8,000 |
Conclusion.
In conclusion, boiler systems are versatile and efficient heating solutions, catering to various needs. Understanding their types, maintenance, and replacement considerations is essential for ensuring comfort and cost-effective operation in your home or facility. If you want to learn about the detailed parameters and cost of boiler systems, please contact us at +0086 186-2391-5479.
FAQs.
How to turn on a boiler heating system?
To start a boiler heating system, ensure the thermostat is set to your desired temperature. Then, locate the power switch or control panel on your boiler and switch it on. Wait for the boiler to ignite, and it will begin heating your home.
How to add water to the boiler system?
To add water to a boiler system, find the system's water inlet valve, typically located near the boiler. Slowly open the valve until the desired water pressure is reached, as indicated on the system's pressure gauge. Be cautious not to overfill.
How to drain a boiler heating system?
To drain a boiler heating system, turn off the boiler and let it cool. Attach a hose to the drain valve, usually found near the bottom of the boiler. Open the valve and let the water discharge into a suitable container or drain until empty.
How to bleed a boiler system?
Bleeding a boiler system is done to remove trapped air. Turn off the boiler, then locate the bleed valves on your radiators or pipes. Open them one at a time until water flows smoothly, then close them once air is expelled.
How to flush the boiler system?
First, turn off the boiler and let it cool. Next, refill it with fresh water while adding a flushing agent. Circulate the water to remove impurities, then drain and refill the system with clean water for optimal performance.
Get your best price
Quickly compare 3 FREE quotes
- Engineer quick quote
- The overall delivery speed is fast
- Financial choice
- Low installation costs and cost savings
25 years+ of boiler R&D
More than 20 innovative technologies